文章目录
- 一、游戏介绍与问题定义
- 1.1 游戏简介
- 1.2 问题定义
- 二、算法介绍
- 2.1 预处理
- 2.1.1 去除背景颜色
- 2.1.2 灰度处理
- 2.2 Q-Learning
- 2.3 神经网络
- 2.4 DQN结构
- 2.4.1 增加样本池
- 2.4.2 利用神经网络计算Q值
- 2.5 组成元素
- 2.6 算法设计
- 2.7.1 Train.py算法
- 2.7.2 test.py算法
- 三、实现方法及参数设置
- 3.1 实现方式
- 3.2 参数设置
- 四、实验结果及分析
- 4.2 各指标关系图
- 4.3 图片数据分析
- 参考文献
- 后记
一、游戏介绍与问题定义
1.1 游戏简介
Flappy Bird游戏需要玩家控制一只小鸟越过管道障碍物。玩家只可以进行“跳跃”或者“不操作”两种操作,即点或不点。点则让小鸟上升一段距离,不点小鸟继续下降。若小鸟碰到障碍物或地面,则游戏失败。
如今,深度学习通过组合低层特征形成更加抽象的高层表示属性类别或特征,以发现数据的分布式特征表示,使得机器学习模型可以直接学习概念,如直接从原始图像数据进行物体类别分类。深层卷积神经网络采用平铺分层卷积滤波器层来模拟视野接受域的影响,在处理计算机视觉问题上,如分类和检测问题,获得了很大成功。本文目的是开发一个深层神经网络模型,具体地,是利用图像中的不同对象训练卷积神经网络,进行基于游戏画面场景状态分析进行图像识别分类。从原始像素中学习游戏的特性,并决定采取相应行动,本质上是一个对游戏场景中特定状态的模式识别过程,在此设计了一个强化学习系统,通过自主学习来玩这款游戏。
1.2 问题定义
当通过很少预定的行为进行编程不能充分解决问题时,可采用强化学习方式,这是一种通过进行场景训练,使算法在输入未知和多维数据(如彩色图片)时做出正确的决策方式。通过这种方式,算法可以学会自动对图像进行特征提取,对于训练中未出现的场景和状态也同样可以进行分类和预测。
二、算法介绍
2.1 预处理
2.1.1 去除背景颜色
实验中Flappy Bird游戏直接输出的像素是288×512的,但为了节省内存将其缩小为84×84大小的图像,每帧图像色阶都是0-255。此外,为了提高卷积神经网络的精度,在这一步去除背景层并用纯黑色背景代替,以去除噪声,如图1所示。

图1 背景使用黑色
2.1.2 灰度处理
依次对所得游戏图像进行缩放、灰度化以及调整亮度处理。在当前帧进入一个状态之前,处理几帧图像叠加组合的多维图像数据(如在模型构建部分提到的),当前帧与先前帧重叠时,灰度稍有降低,当我们远离最新帧时强度降低。因此,这样输入的图像将提供关于小鸟当前所在轨迹的良好信息,其处理过程如图2所示。

图2 图像处理
2.2 Q-Learning
强化学习的目标是使总回报(奖励)最大化。在Q-Learning中,它是非策略的,迭代更新使用的是贝尔曼方程,获得Q值的目标值,


其中s′和a′ 分别是下一帧的状态和动作(1或0),r是奖励(-1,0.1,1),γ是折扣因子。Qi(s,a)是为( s , a )矩阵在第i次迭代的Q值。这种更新迭代将收敛得到一个最佳的Q函数。为了防止学习僵化,这个动作值函数可以用一个函数(这里为深度学习网络)近似,以便能更好概括不可预见的状态。
学习算法的输入点由[state ,action ,reward , next _ state,ternmial ]列表构成,函数能够通过这些输入点来构建一个能最大限度提高整体回报并以此预测动作的模型。将这里的函数构建为一个卷积神经网络,并使用上述方程中的更新规则更新其参数。以下方程为使用mseloss损失函数及来模拟这个函数。

均方误差(mean square error, MSE),是反应估计量与被估计量之间差异程度的一种度量,设t 是根据子样确定的总体参数θ 的一个估计量,〖(θ-t)〗_^2 的数学期望,称为估计量t 的均方误差。

2.3 神经网络
如图3所示,在当前模型结构中, 首先有三个卷积层,然后是两个完全连接层,最终完全连接层的输出是两个动作的得分,结果由损失函数得出。 损失函数自动进行Q学习参数设置。遵循空间批量规范,在每个卷积层后都添加ReLu。 输入图像的大小84×84,每个时刻有两种可能的输出操作,每次动作将会获得一个得分值,以此决定最佳动作。


图1 图像resize成84×84大小 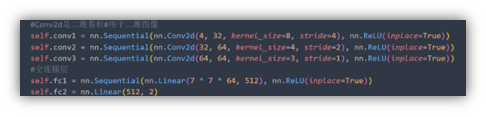

图2 神经网络设计
2.4 DQN结构
将Q学习与深度学习结合,使用深度神经网络来建模Q值函数

2.4.1 增加样本池
在Q-Learning中,以连续方式记录的经验数据是高度相关的。若使用相同的顺序更新DQN参数,训练过程就会受到干扰。与从一个标记的数据集中采样小批量训练分类模型类似,这里同样应该在抽取出的获得更新的DQN经验中引入一定的随机性。为此设置一个经验回放存储器,用来存储每帧游戏画面的经验数据,直到达到其最大存储容量。在DQN理论介绍时提到,DQN的一大特点就是设置了数据库,后续的每次训练从数据库中抽取数据。这样可以使得训练更加有效。
程序中,使用了一个队列replay_memory来当作经验池,经验池大小replay_memory_size
设置为30000(如果太大,电脑内存不够… …),如果数据库容量达到上限,将会把最先进入的数据抛出,即队列的先入先出。


2.4.2 利用神经网络计算Q值
输入状态值,输出为Q值,根据大量的数据去训练神经网络的参数,最终得到Q-Learning的计算模型。

2.5 组成元素
智能体(agent)
强化学习的本体,作为学习者或者决策者。
环境(environment)
强化学习智能体以外的一切,主要由状态集合组成。
状态(state)
一个表示环境的数据,状态集则是环境中所有可能的状态。
动作(action)
智能体可以做出的动作,动作集则是智能体可以做出的所有动作。
奖励(reward)
智能体在执行一个动作后,获得的正/负反馈信号,奖励集则是智能体可以获得的所有反馈信息。

2.6 算法设计
2.7.1 Train.py算法
开启游戏模拟器,会打开一个窗口,实时显示游戏的信息,获取游戏的状态
创建样本池
当训练次数小于设置的迭代次数(300万)时,进入训练
获得的第一个数值, 也就是从神经网络当中的q数值
执行一个随机动作或者神经网络计算的Q(s,a)值选择对应的动作
样本池使用一个大小确定的队列来进行维护,其中存放的是游戏过程中的数据state, action, reward, next_state, terminal
得到下一帧图像进行数据预处理
每执行一次动作,游戏会返回执行该动作之后的一帧图像,把样本池更新,若样本池已满,则将最早存入的数据替换出去
从记忆库中随机获得batch_size个数据进行训练
DQN算法
- 初始化Q函数Q,目标Q函数Q ̂= Q对于每一个回合
- 对于每一个时间步iter
- 探索与利用(随着训练的次数越来越多,Q值函数越来越精确,比较能确定较好的动作,把epsilon的值变小,减少探索,即较少随机决定动作)
- 对于给定的状态state ,基于Q (epsilon – 贪心)执行动作action。
- 获得反馈reward,并获得新的状态next_state。
- 将(state, action , reward , next_state)存储到缓冲区中(更新经验池)。
- 从缓冲区中采样(通常以批量形式)( state, action , reward , next_state)。
- 目标值是y = reward + 〖max〗_a Q ̂ (state , action)。
- 对于每一个时间步iter
- 更新Q的参数使得Q(state , action)尽可能接近于回归。
- 每C步重置Q ̂=Q。
2.7.2 test.py算法
使用train.py每隔50000次训练产生保存的模型,产生游戏对应画面的下一个动作,累计计算得分,直到小鸟掉落或撞管道换下一个模型测试,最后根据每个模型的得分,产生得分曲线图。
三、实现方法及参数设置
3.1 实现方式
4个代码文件与多个游戏图片文件,utils.py负责图像的基本处理;deep_q_network.py负责神经网络的设计,产生各状态的得分;flappy_bird.py负责游戏的处理,更新画面等;train.py负责训练、产生模型,更新神经网络等;test.py用于测试。

图4 源码联系
3.2 参数设置
模型参数:Flappy Bird游戏每秒播放30帧,最近的4帧图像处理后进行组合,生成一个状态;贴现因子γ 设置为0.99;
奖励设置:通过管道reward = + 1.0, 撞到管道或地面reward = -1.0,其他时候reward = 0.1。
DQN参数:探索概率 epsilon 在2000000更新中从0.1线性下降到0。回放存储器的大小设置为30000,批处理大小为32。
训练参数:来更新DQN参数的梯度下降更新法是学习率为1e^(-6)的Adam优化器。在试错基础上选择这些参数,用来观察损失值的收敛性。
四、实验结果及分析
4.1 测试结果
几个典型阶段:
- 迭代5万次,通过管道获取的奖励少,小鸟一直向上飞(直接摆烂… …),几乎一个管道通过不了;
- 迭代50万次,偶尔可以通过一两个管道;
- 迭代100万次,可以通过4、5个管道;
- 迭代150万次,可以通过超过15个管道;
- 迭代250万次,可以一直通过管道,极少数会失误; 迭代300万次,小鸟一直向前飞… …

以下是各个不同训练阶段(每隔5万次产生一个模型)的测试结果

由于有的训练模型小鸟会一直飞下去,为了加快测试进度,选取70分的阈值,代表小鸟可以一直飞下去,可以观察到250万次的迭代后,模型性能已经很不错了。训练迭代的次数指的是DQN更新的次数 ,同时可以看出,更多的训练次数并不意味着一定能提高模型预测结果的准确性(比如210万次迭代产生的模型没有180万次迭代产生的模型好)。实际上,更多次的训练存在许多不稳定性以及结果振荡情况,过多次数的训练,模型会出现过拟合情况。
4.2 各指标关系图
训练结束后,用模型测试了一些游戏状态,以检测是否能得出合理的结果。代码中使用的SummaryWriter函数可以记录loss, Epsilon, reward, Q值 与迭代次数的关系,如图

4.3 图片数据分析
随着迭代次数的增加,
(1)epsilon线性减小,减少探索;
(2)loss函数总体下降,表明预测值与真实值之间的差距减小,同时训练一段时间后表现为极其缓慢的下降,然后平稳,说明训练次数充足;
(3)Q值随迭代次数一直增加;
(4)Reward基本不变。
五、实验代码
deep_q_network.py
import torch.nn as nnclass DeepQNetwork(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(DeepQNetwork, self).__init__()#使用torch.nn.Sequential可以快速的搭建一个神经网络#Conv2d是二维卷积#用于二维图像self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(4, 32, kernel_size=8, stride=4), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=4, stride=2), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))#全连接层self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(7 * 7 * 64, 512), nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 2)self._create_weights()def _create_weights(self):for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d) or isinstance(m, nn.Linear):nn.init.uniform_(m.weight, -0.01, 0.01)nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)def forward(self, input):output = self.conv1(input)output = self.conv2(output)output = self.conv3(output)output = output.view(output.size(0), -1)output = self.fc1(output)output = self.fc2(output)return outputflappy_bird.py
from itertools import cyclefrom time import sleepfrom numpy.random import randintfrom pygame import Rect, init, time, displayfrom pygame.event import pumpfrom pygame.image import loadfrom pygame.surfarray import array3d, pixels_alphafrom pygame.transform import rotateimport numpy as npclass FlappyBird(object):init()#游戏时间fps_clock = time.Clock()screen_width = 288screen_height = 512screen = display.set_mode((screen_width, screen_height))display.set_caption('强化学习Flappy Bird')base_image = load('base.png').convert_alpha()background_image = load('background-black.png').convert()pipe_images = [rotate(load('pipe-green.png').convert_alpha(), 180), load('pipe-green.png').convert_alpha()]bird_images = [load('redbird-downflap.png').convert_alpha(), load('redbird-midflap.png').convert_alpha(), load('redbird-upflap.png').convert_alpha()]# number_images = [load('assets/sprites/{}.png'.format(i)).convert_alpha() for i in range(10)]bird_hitmask = [pixels_alpha(image).astype(bool) for image in bird_images]pipe_hitmask = [pixels_alpha(image).astype(bool) for image in pipe_images]#每秒传输帧数fps = 30pipe_gap_size = 100pipe_velocity_x = -4# 鸟的元素min_velocity_y = -8max_velocity_y = 10downward_speed = 1upward_speed = -9bird_index_generator = cycle([0, 1, 2, 1])def __init__(self):#初始化小鸟、管子self.iter = self.bird_index = self.score = 0self.bird_width = self.bird_images[0].get_width()self.bird_height = self.bird_images[0].get_height()self.pipe_width = self.pipe_images[0].get_width()self.pipe_height = self.pipe_images[0].get_height()self.bird_x = int(self.screen_width / 5)self.bird_y = int((self.screen_height - self.bird_height) / 2)#地的初始位置self.base_x = 0self.base_y = self.screen_height * 0.79self.base_shift = self.base_image.get_width() - self.background_image.get_width()pipes = [self.generate_pipe(), self.generate_pipe()]pipes[0]["x_upper"] = pipes[0]["x_lower"] = self.screen_widthpipes[1]["x_upper"] = pipes[1]["x_lower"] = self.screen_width * 1.5self.pipes = pipesself.current_velocity_y = 0self.is_flapped = Falsedef generate_pipe(self):x = self.screen_width + 10gap_y = randint(2, 10) * 10 + int(self.base_y / 5)return {"x_upper": x, "y_upper": gap_y - self.pipe_height, "x_lower": x, "y_lower": gap_y + self.pipe_gap_size}def is_collided(self):# 检查鸟是否触地if self.bird_height + self.bird_y + 1 >= self.base_y:return Truebird_bbox = Rect(self.bird_x, self.bird_y, self.bird_width, self.bird_height)pipe_boxes = []for pipe in self.pipes:pipe_boxes.append(Rect(pipe["x_upper"], pipe["y_upper"], self.pipe_width, self.pipe_height))pipe_boxes.append(Rect(pipe["x_lower"], pipe["y_lower"], self.pipe_width, self.pipe_height))# 检查鸟的边框是否与任何管道的边框重叠 if bird_bbox.collidelist(pipe_boxes) == -1:return Falsefor i in range(2):cropped_bbox = bird_bbox.clip(pipe_boxes[i])min_x1 = cropped_bbox.x - bird_bbox.xmin_y1 = cropped_bbox.y - bird_bbox.ymin_x2 = cropped_bbox.x - pipe_boxes[i].xmin_y2 = cropped_bbox.y - pipe_boxes[i].yif np.any(self.bird_hitmask[self.bird_index][min_x1:min_x1 + cropped_bbox.width, min_y1:min_y1 + cropped_bbox.height] * self.pipe_hitmask[i][min_x2:min_x2 + cropped_bbox.width,min_y2:min_y2 + cropped_bbox.height]):#print("game over")return Truereturn Falsedef next_frame(self, action):pump()reward = 0.1terminal = False# 检查输入动作if action == 1:self.current_velocity_y = self.upward_speedself.is_flapped = True# 更新分数bird_center_x = self.bird_x + self.bird_width / 2for pipe in self.pipes:pipe_center_x = pipe["x_upper"] + self.pipe_width / 2if pipe_center_x < bird_center_x < pipe_center_x + 5:self.score += 1reward = 1break# 更新 index and iterationif (self.iter + 1) % 3 == 0:self.bird_index = next(self.bird_index_generator)self.iter = 0self.base_x = -((-self.base_x + 100) % self.base_shift)# 更新鸟位置if self.current_velocity_y < self.max_velocity_y and not self.is_flapped:self.current_velocity_y += self.downward_speedif self.is_flapped:self.is_flapped = Falseself.bird_y += min(self.current_velocity_y, self.bird_y - self.current_velocity_y - self.bird_height)if self.bird_y < 0:self.bird_y = 0# 更新管道位置for pipe in self.pipes:pipe["x_upper"] += self.pipe_velocity_xpipe["x_lower"] += self.pipe_velocity_x# 更新管道if 0 < self.pipes[0]["x_lower"] < 5:self.pipes.append(self.generate_pipe())if self.pipes[0]["x_lower"] < -self.pipe_width:del self.pipes[0]if self.is_collided():terminal = Truereward = -1self.__init__()# 绘制到窗口self.screen.blit(self.background_image, (0, 0))self.screen.blit(self.base_image, (self.base_x, self.base_y))self.screen.blit(self.bird_images[self.bird_index], (self.bird_x, self.bird_y))for pipe in self.pipes:self.screen.blit(self.pipe_images[0], (pipe["x_upper"], pipe["y_upper"]))self.screen.blit(self.pipe_images[1], (pipe["x_lower"], pipe["y_lower"]))image = array3d(display.get_surface())display.update()self.fps_clock.tick(self.fps)return image, reward, terminalutils.py
import cv2import numpy as npdef pre_processing(image, width, height):#图片变灰image = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(image, (width, height)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)#进行阈值二值化操作,大于阈值1的,使用255表示, 小于阈值1的,使用0表示_, image = cv2.threshold(image, 1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)print(image)return image[None, :, :].astype(np.float32)train.py
import argparseimport osimport shutilfrom random import random, randint, sampleimport numpy as npfrom sklearn.metrics import log_lossimport torchimport torch.nn as nnfrom tensorboardX import SummaryWriterfrom src.deep_q_network import DeepQNetworkfrom src.flappy_bird import FlappyBirdfrom src.utils import pre_processingimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef get_args():parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("""Implementation of Deep Q Network to play Flappy Bird""")parser.add_argument("--image_size", type=int, default=84, help="所有图像的公共宽度和高度")#批大小32parser.add_argument("--batch_size", type=int, default=32, help="每批的图像数")parser.add_argument("--optimizer", type=str, choices=["sgd", "adam"], default="adam")parser.add_argument("--lr", type=float, default=1e-6)parser.add_argument("--gamma", type=float, default=0.99)parser.add_argument("--initial_epsilon", type=float, default=0.1)parser.add_argument("--final_epsilon", type=float, default=1e-4)##迭代次数parser.add_argument("--num_iters", type=int, default=2000000)parser.add_argument("--replay_memory_size", type=int, default=30000, help="测试阶段之间的epoches数")parser.add_argument("--log_path", type=str, default="tensorboard")parser.add_argument("--saved_path", type=str, default="./")args = parser.parse_args()return argsdef train(opt):if torch.cuda.is_available(): # 使用GPU加快速度#print("1")torch.cuda.manual_seed(123)else:torch.manual_seed(123)model = DeepQNetwork()#model = torch.load("{}/flappy_bird_1000000".format(opt.saved_path), map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage)if os.path.isdir(opt.log_path):shutil.rmtree(opt.log_path)os.makedirs(opt.log_path)writer = SummaryWriter(opt.log_path)optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=opt.lr)criterion = nn.MSELoss()game_state = FlappyBird()image, reward, terminal = game_state.next_frame(0)image = pre_processing(image[:game_state.screen_width, :int(game_state.base_y)], opt.image_size, opt.image_size)image = torch.from_numpy(image)if torch.cuda.is_available():#print("2")model.cuda()image = image.cuda()state = torch.cat(tuple(image for _ in range(4)))[None, :, :, :]replay_memory = []'''loss_memory = []iter_num = []'''iter = 0while iter < opt.num_iters:#prediction = max(s,a)prediction = model(state)[0]# Exploration or exploitationepsilon = opt.final_epsilon + ((opt.num_iters - iter) * (opt.initial_epsilon - opt.final_epsilon) / opt.num_iters)u = random()random_action = u <= epsilonif random_action:print("随机产生一个动作")#产生的动作随着iter增大而减少action = randint(0, 1)#Explorationelse:action = torch.argmax(prediction).item()#exploitationnext_image, reward, terminal = game_state.next_frame(action)next_image = pre_processing(next_image[:game_state.screen_width, :int(game_state.base_y)], opt.image_size,opt.image_size)#数组转换成张量,且二者共享内存,对张量进行修改比如重新赋值,那么原始数组也会相应发生改变。next_image = torch.from_numpy(next_image)# 在给定维度上对输⼊的张量state进⾏连接操作。if torch.cuda.is_available():#print("3")next_image = next_image.cuda()next_state = torch.cat((state[0, 1:, :, :], next_image))[None, :, :, :]replay_memory.append([state, action, reward, next_state, terminal])if len(replay_memory) > opt.replay_memory_size:del replay_memory[0] # 更新样本池# 从序列replay_memory中随机抽取min(len(replay_memory), opt.batch_size)个元素, 以list形式返回#训练的一批,一次iterationbatch = sample(replay_memory, min(len(replay_memory), opt.batch_size))state_batch, action_batch, reward_batch, next_state_batch, terminal_batch = zip(*batch)# 连接操作state_batch = torch.cat(tuple(state for state in state_batch))#数组转换成张量action_batch = torch.from_numpy(np.array([[1, 0] if action == 0 else [0, 1] for action in action_batch], dtype=np.float32))#数组转换成张量reward_batch = torch.from_numpy(np.array(reward_batch, dtype=np.float32)[:, None])next_state_batch = torch.cat(tuple(state for state in next_state_batch))if torch.cuda.is_available():#print("4")state_batch = state_batch.cuda()action_batch = action_batch.cuda()reward_batch = reward_batch.cuda()next_state_batch = next_state_batch.cuda()current_prediction_batch = model(state_batch)next_prediction_batch = model(next_state_batch)# 连接操作y_batch张量y_batch = torch.cat( # 贝尔曼方程tuple(reward if terminal else reward + opt.gamma * torch.max(prediction) for reward, terminal, prediction inzip(reward_batch, terminal_batch, next_prediction_batch)))#当前值q_value张量q_value = torch.sum(current_prediction_batch * action_batch, dim=1)optimizer.zero_grad()#用的梯度包含上一个batch的,相当于batch_size为之前的两倍,所以optimizer.step()是用在batch里的# y_batch = y_batch.detach()# 损失函数MSELoss,计算目标的均方根误差# loss = 1/n*sum(q_value-y_batch)**2loss = criterion(q_value, y_batch)loss.backward()# 根据网络反向传播的梯度信息来更新网络的参数optimizer.step()# 更新学习率的#状态更新state = next_stateiter += 1print(iter)'''print("Iteration: {}/{}, Action: {}, Loss: {}, Epsilon {}, Reward: {}, Q-value: {}".format(iter + 1,opt.num_iters,action,loss,epsilon, reward, torch.max(prediction)))'''# 记录生成图片writer.add_scalar('Train/Loss', loss, iter)writer.add_scalar('Train/Epsilon', epsilon, iter)writer.add_scalar('Train/Reward', reward, iter)writer.add_scalar('Train/Q-value', torch.max(prediction), iter)'''if(iter+1) % 500 == 0:#迭代500次采样一次loss,形成loss函数曲线loss_memory.append(np.double(format(loss)))iter_num.append(iter+1)'''if (iter+1) % 50000 == 0:#输出60个模型print(iter+1)torch.save(model, "{}/flappy_bird_{}".format(opt.saved_path, iter+1))'''if (iter+1) % 1000000 == 0:#共采样2000个点plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)plt.ylabel('Recon_loss')plt.xlabel('iter_num')#print(iter_num,loss_memory)plt.plot(iter_num,loss_memory)plt.savefig("{}/flappy_bird_{}.jpg".format(opt.saved_path, iter+1))'''torch.save(model, "{}/flappy_bird_{}".format(opt.saved_path, iter+1))if __name__ == "__main__":opt = get_args()train(opt) test.py
import argparsefrom email import iteratorsimport torchfrom time import sleepfrom src.deep_q_network import DeepQNetworkfrom src.flappy_bird import FlappyBirdfrom src.utils import pre_processingimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltdef get_args():parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("""Implementation of Deep Q Network to play Flappy Bird""")parser.add_argument("--image_size", type=int, default=84, help="The common width and height for all images")parser.add_argument("--saved_path", type=str, default="./")args = parser.parse_args()return argsdef test(opt,i,game_num,game_sore):torch.manual_seed(123)model = torch.load("{}/flappy_bird_{}0000".format(opt.saved_path,i), map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage)model.eval()game_state = FlappyBird()image, reward, terminal = game_state.next_frame(0)image = pre_processing(image[:game_state.screen_width, :int(game_state.base_y)], opt.image_size, opt.image_size)image = torch.from_numpy(image)state = torch.cat(tuple(image for _ in range(4)))[None, :, :, :]while True:if reward == -1 or game_sore > 350:game_num += 1if(game_num==5):return game_sore//5game_sore += rewardprediction = model(state)[0]action = torch.argmax(prediction).item()#print(time)next_image, reward, terminal = game_state.next_frame(action)next_image = pre_processing(next_image[:game_state.screen_width, :int(game_state.base_y)], opt.image_size,opt.image_size)next_image = torch.from_numpy(next_image)next_state = torch.cat((state[0, 1:, :, :], next_image))[None, :, :, :]state = next_stateif __name__ == "__main__":opt = get_args()iteration = []game_Sore = []for i in range(5,301,5):game_num = 0game_sore = 0game_sore = test(opt,i,game_num,game_sore)iteration.append(i*10000)game_Sore.append(game_sore)print("迭代",i*10000," 奖励",game_sore)plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8), dpi=80)plt.ylabel('平均得分')plt.xlabel('迭代次数')plt.plot(iteration,game_Sore)plt.savefig("iteration-game_Sore.jpg")参考文献
[1] Chen K . Deep Reinforcement Learning for Flappy Bird.
后记
很久很久以前,大三下的《数据融合与智能分析》实验报告,其实我到现在也没太懂强化学习(还是要读书呀,看论文呀。。。)