日常工作中 Map 绝对是我们 Java 程序员高频使用的一种数据结构,那 Map 都有哪些遍历方式呢?这篇文章阿粉就带大家看一下,看看你经常使用的是哪一种。
通过 entrySet 来遍历1、通过 for 和 map.entrySet() 来遍历
第一种方式是采用 for 和 Map.Entry 的形式来遍历,通过遍历 map.entrySet() 获取每个 entry 的 key 和 value,代码如下。这种方式一般也是阿粉使用的比较多的一种方式,没有什么花里胡哨的用法,就是很朴素的获取 map 的 key 和 value。
public static void testMap1(Map map) { long sum = 0; for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) { sum += entry.getKey() + entry.getValue(); } System.out.println(sum); }看过 HashMap 源码的同学应该会发现,这个遍历方式在源码中也有使用,如下图所示,
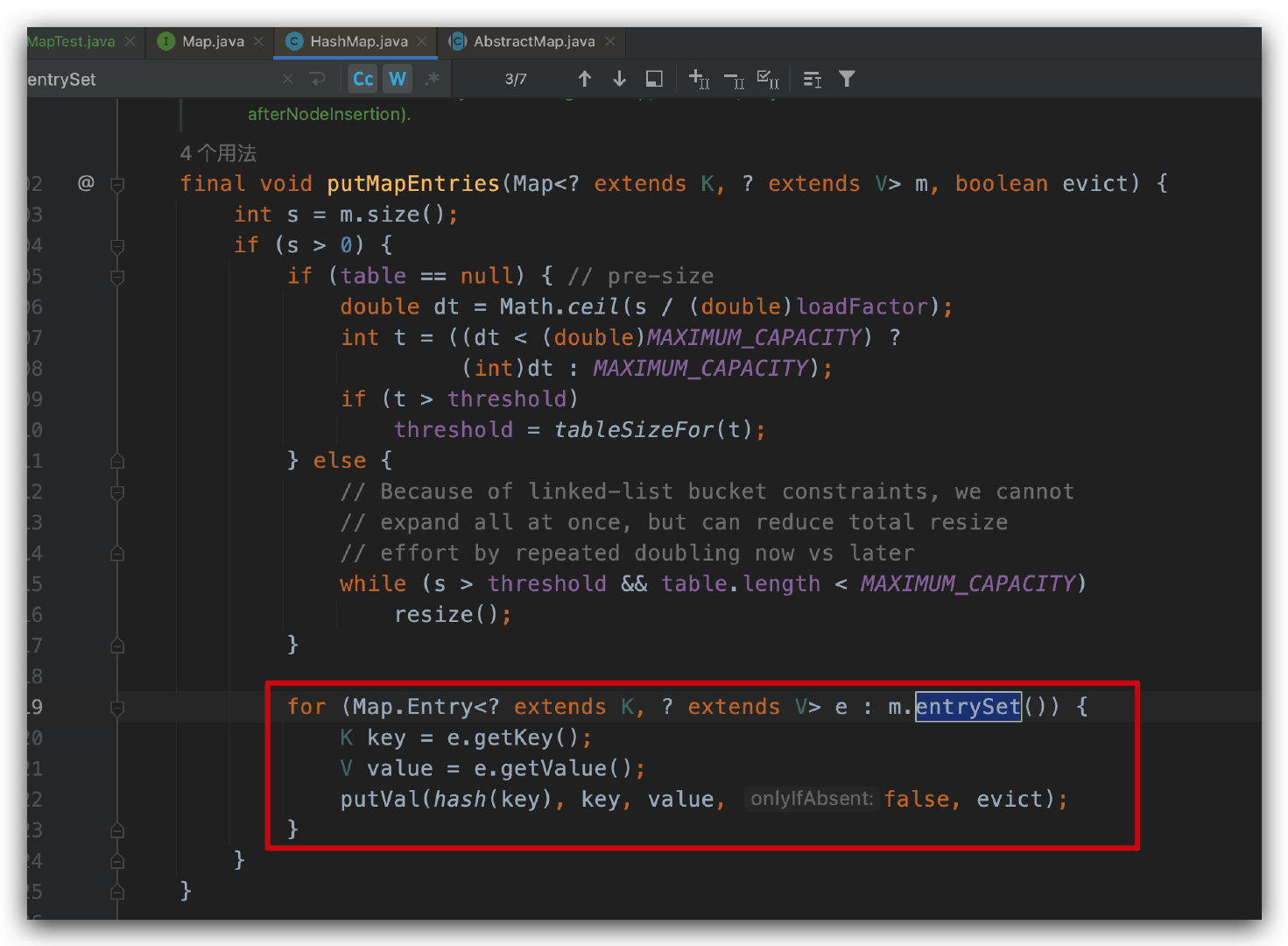
putMapEntries 方法在我们调用 putAll 方法的时候会用到。

2、通过 for, Iterator 和 map.entrySet() 来遍历
我们第一个方法是直接通过 for 和 entrySet() 来遍历的,这次我们使用 entrySet() 的迭代器来遍历,代码如下。
public static void testMap2(Map map) { long sum = 0; for (Iterator<Map.Entry> entries = map.entrySet().iterator(); entries.hasNext(); ) { Map.Entry entry = entries.next(); sum += entry.getKey() + entry.getValue(); } System.out.println(sum); }3、通过 while,Iterator 和 map.entrySet() 来遍历
上面的迭代器是使用 for 来遍历,那我们自然可以想到还可以用 while 来进行遍历,所以代码如下所示。
public static void testMap3(Map map) { Iterator<Map.Entry> it = map.entrySet().iterator(); long sum = 0; while (it.hasNext()) { Map.Entry entry = it.next(); sum += entry.getKey() + entry.getValue(); } System.out.println(sum); }这种方法跟上面的方法类似,只不过循环从 for 换成了 while,日常我们在开发的时候,很多场景都可以将 for 和 while 进行替换。2 和 3 都使用迭代器 Iterator,通过迭代器的 next(),方法来获取下一个对象,依次判断是否有 next。
通过 keySet 来遍历
上面的这三种方式虽然代码的写法不同,但是都是通过遍历 map.entrySet() 来获取结果的,殊途同归。接下来我们看另外的一组。
4、通过 for 和 map.keySet() 来遍历
前面的遍历是通过 map.entrySet() 来遍历,这里我们通过 map.keySet() 来遍历,顾名思义前者是保存 entry 的集合,后者是保存 key 的集合,遍历的代码如下,因为是 key 的集合,所以如果想要获取 key 对应的 value 的话,还需要通过 map.get(key) 来获取。
public static void testMap4(Map map) { long sum = 0; for (Integer key : map.keySet()) { sum += key + map.get(key); } System.out.println(sum); }5、通过 for,Iterator 和 map.keySet() 来遍历
public static void testMap5(Map map) { long sum = 0; for (Iterator key = map.keySet().iterator(); key.hasNext(); ) { Integer k = key.next(); sum += k + map.get(k); } System.out.println(sum); }6、通过 while,Iterator 和 map.keySet() 来遍历
public static void testMap6(Map map) { Iterator it = map.keySet().iterator(); long sum = 0; while (it.hasNext()) { Integer key = it.next(); sum += key + map.get(key); } System.out.println(sum); }我们可以看到这种方式相对于 map.entrySet() 方式,多了一步 get 的操作,这种场景比较适合我们只需要 key 的场景,如果也需要使用 value 的场景不建议使用 map.keySet() 来进行遍历,因为会多一步 map.get() 的操作。
Java 8 的遍历方式
注意下面的几个遍历方法都是是 JDK 1.8 引入的,如果使用的 JDK 版本不是 1.8 以及之后的版本的话,是不支持的。
7、通过 map.forEach() 来遍历
JDK 中的 forEach 方法,使用率也挺高的。
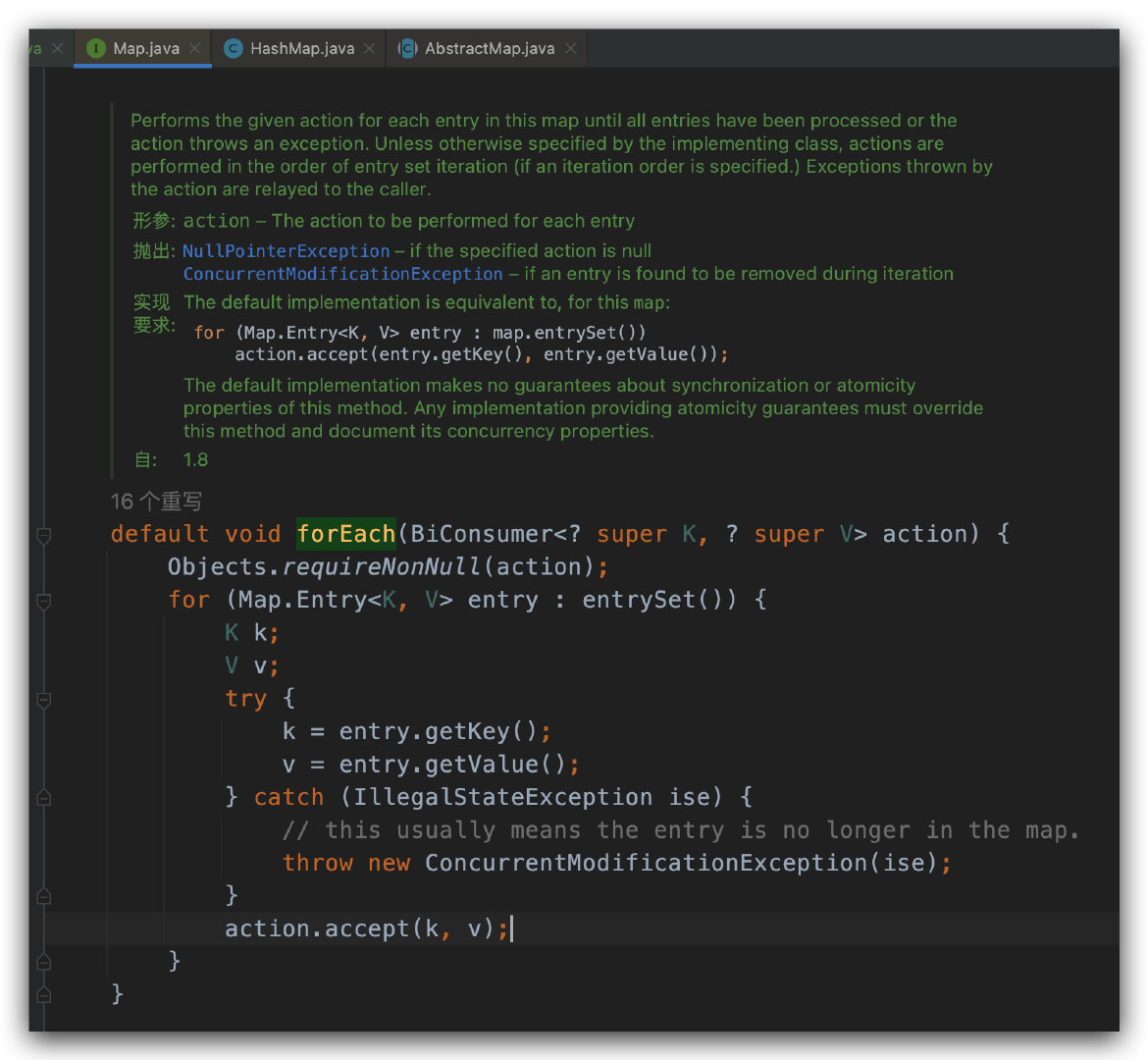
public static void testMap7(Map map) { final long[] sum = {0}; map.forEach((key, value) -> { sum[0] += key + value; }); System.out.println(sum[0]); }该方法被定义在 java.util.Map#forEach 中,并且是通过 default 关键字来标识的,如下图所示。这里提个问题,为什么要使用 default 来标识呢?欢迎把你的答案写在评论区。
8、Stream 遍历
public static void testMap8(Map map) { long sum = map.entrySet().stream().mapToLong(e -> e.getKey() + e.getValue()).sum(); System.out.println(sum); }9、ParallelStream 遍历
public static void testMap9(Map map) { long sum = map.entrySet().parallelStream().mapToLong(e -> e.getKey() + e.getValue()).sum(); System.out.println(sum); }这两种遍历方式都是 JDK 8 的 Stream 遍历方式,stream 是普通的遍历,parallelStream 是并行流遍历,在某些场景会提升性能,但是也不一定。
测试代码
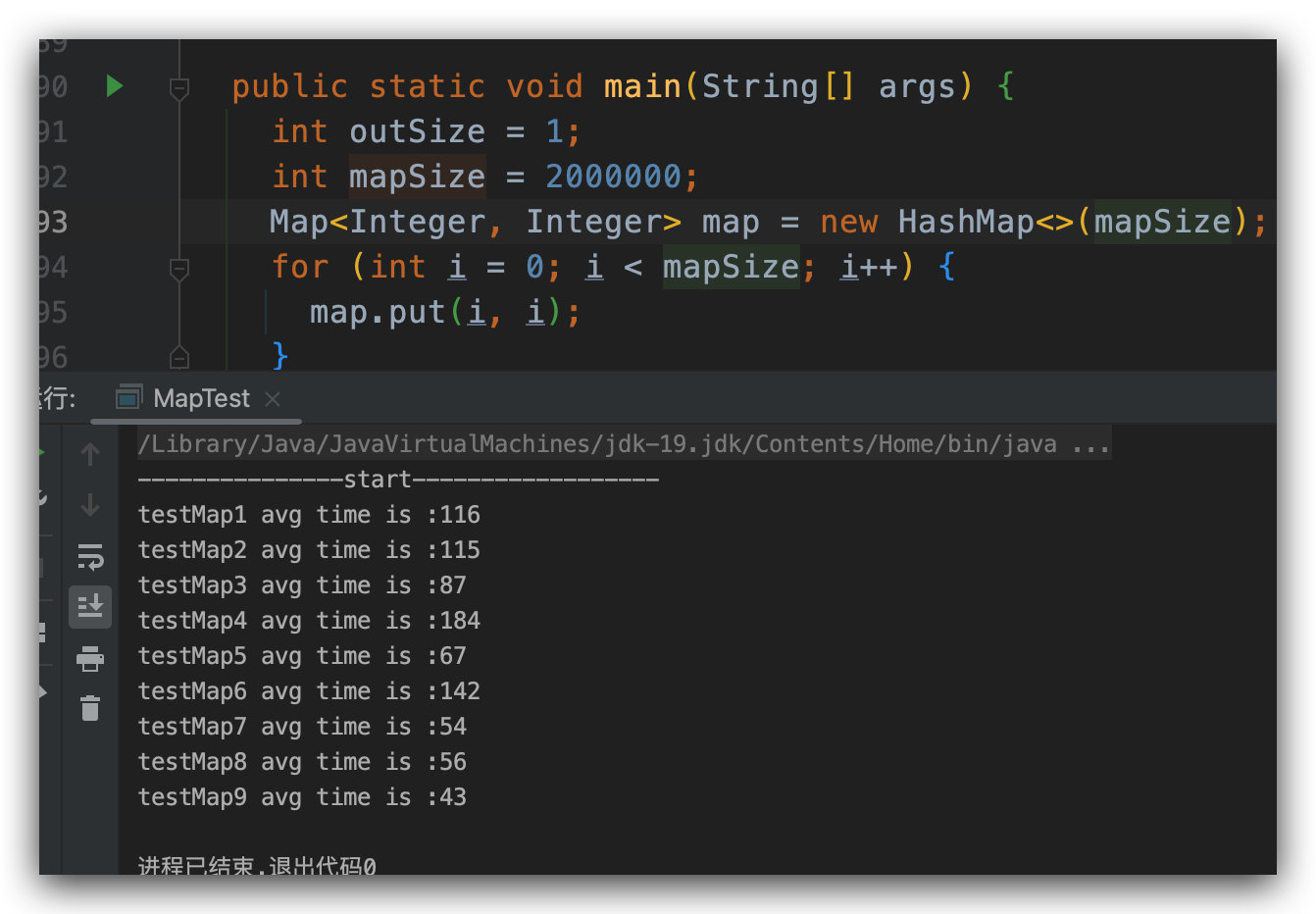
上面的遍历方式有了,那么我们在日常开发中到底该使用哪一种呢?每一种的性能是怎么样的呢?为此阿粉这边通过下面的代码,我们来测试一下每种方式的执行时间。
public static void main(String[] args) { int outSize = 1; int mapSize = 200; Map map = new HashMap(mapSize); for (int i = 0; i 0; size--) { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); testMap1(map); totalTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; } System.out.println("testMap1 avg time is :" + (totalTime / outSize));// 省略其他方法,代码跟上面一致}为了避免一些干扰,这里通过外层的 for 来进行多次计算,然后求平均值,当我们的参数分别是 outSize = 1,mapSize = 200 的时候,测试的结果如下
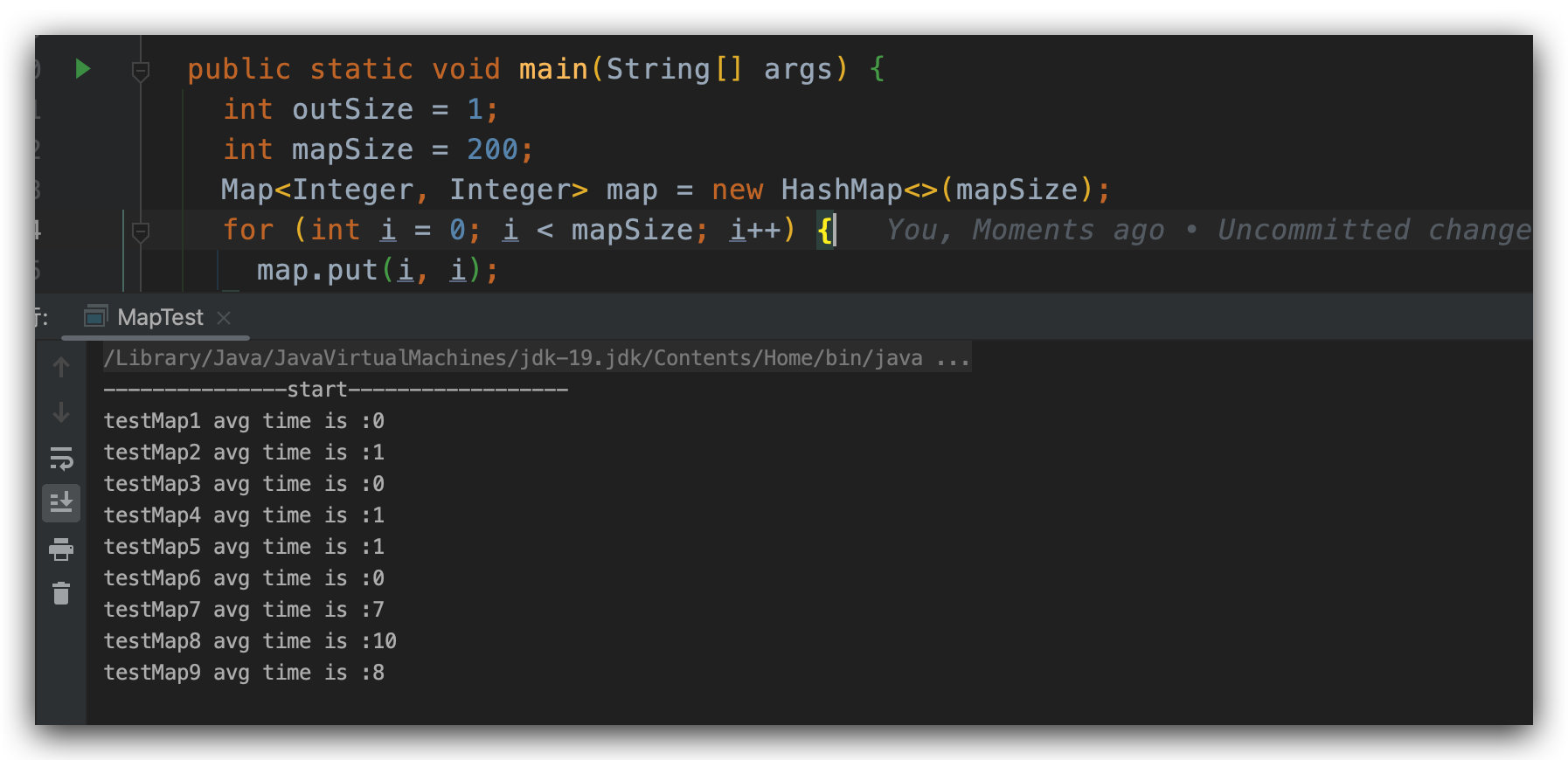
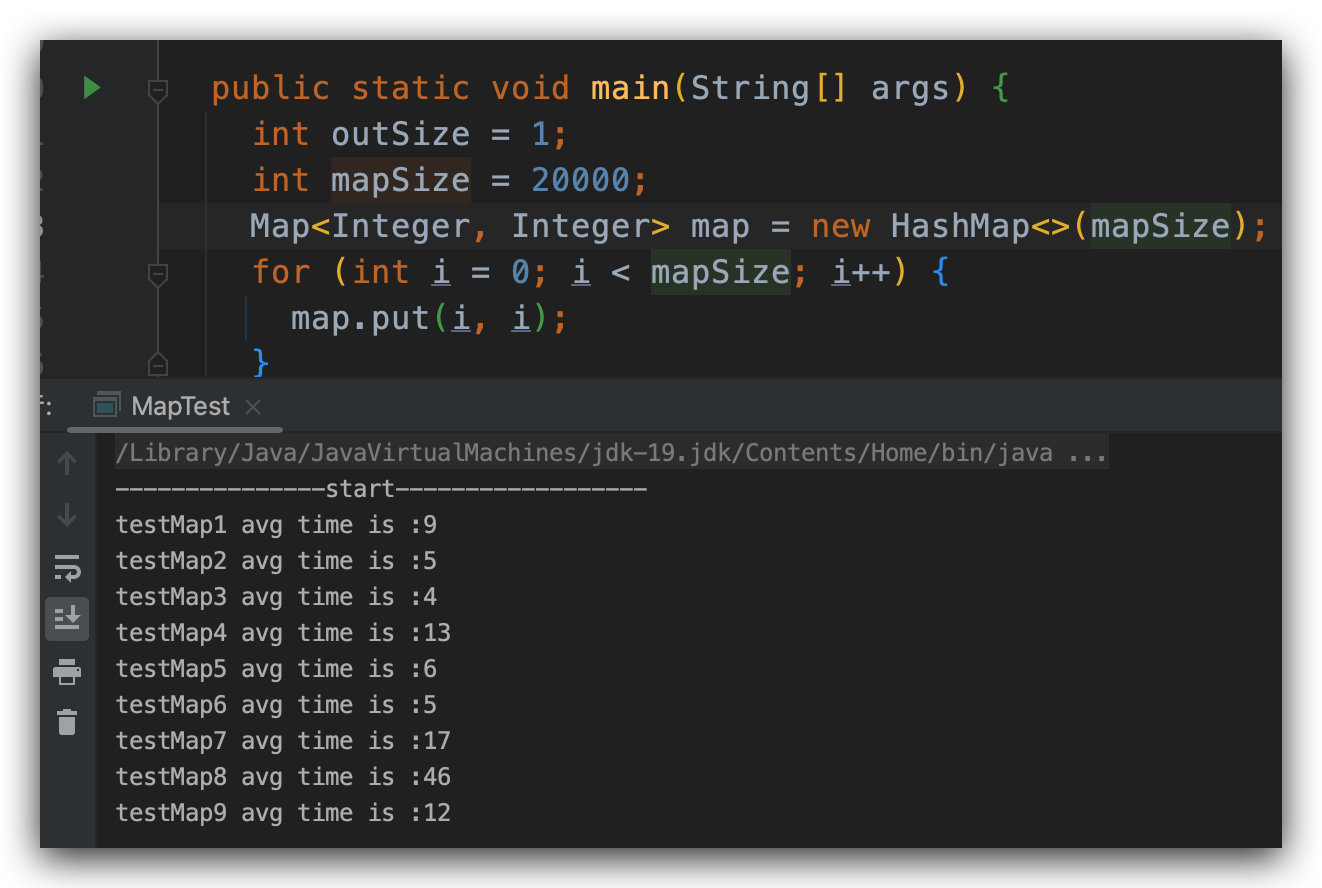
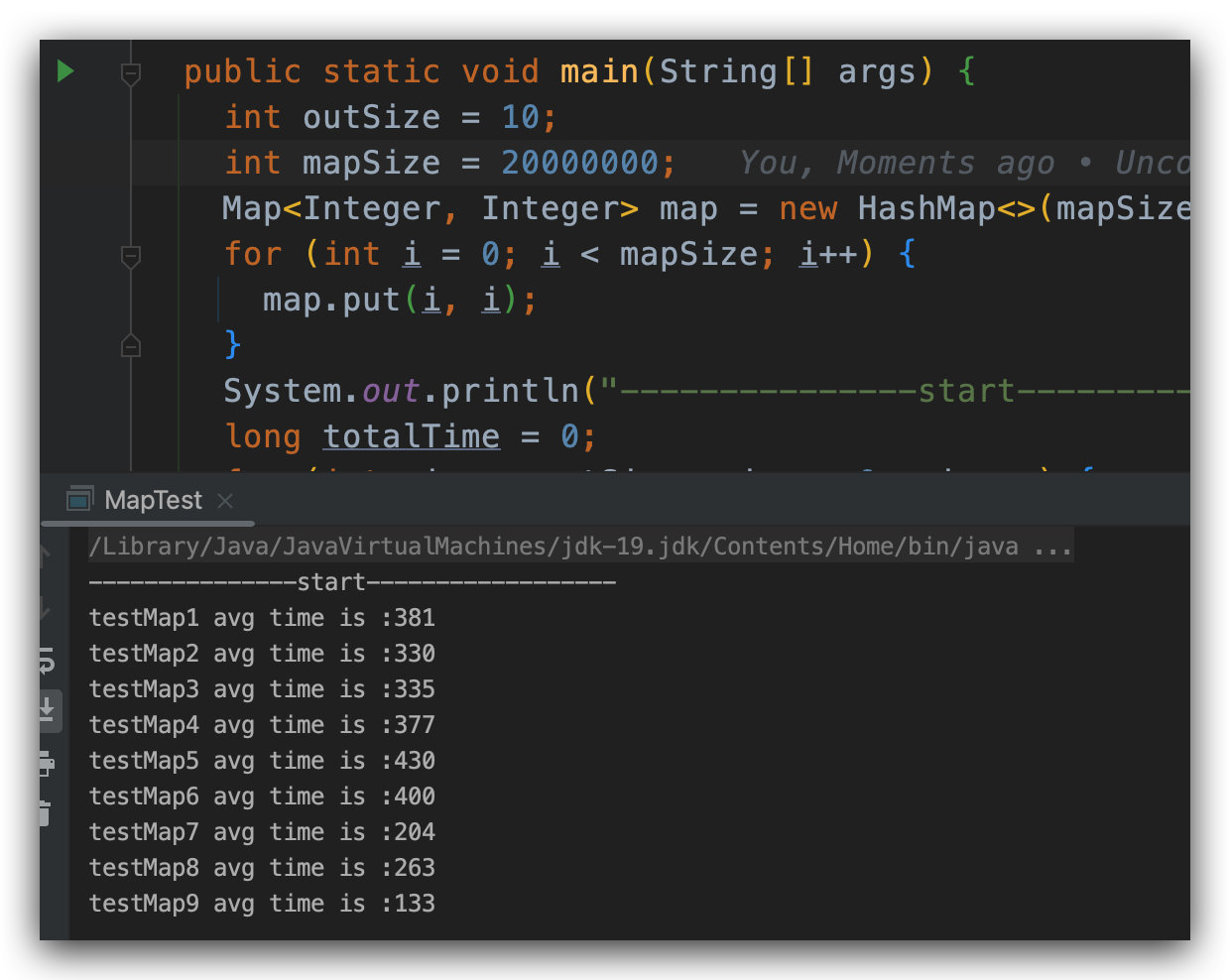
当随着我们增大 mapSize 的时候,我们会发现,后面几个方法的性能是逐渐上升的。
总结
从上面的例子来看,当我们的集合数量很少的时候,基本上普通的遍历就可以搞定,不需要使用 JDK 8 的高级 API 来进行遍历,当我们的集合数量较大的时候,就可以考虑采用 JDK 8 的 forEach 或者 Stream 来进行遍历,这样的话效率更高。在普通的遍历方法中 entrySet() 的方法要比使用 keySet() 的方法好。
本文来自博客园,作者:zi-you,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zi-you/p/16920311.html