Struts2是一个基于MVC设计模式设计模式的Web应用框架应用框架,它本质上相当于一个servlet,在MVC设计模式中,Struts2作为控制器(Controller)来建立模型与视图的数据交互。
Struts2处理请求流程如下:
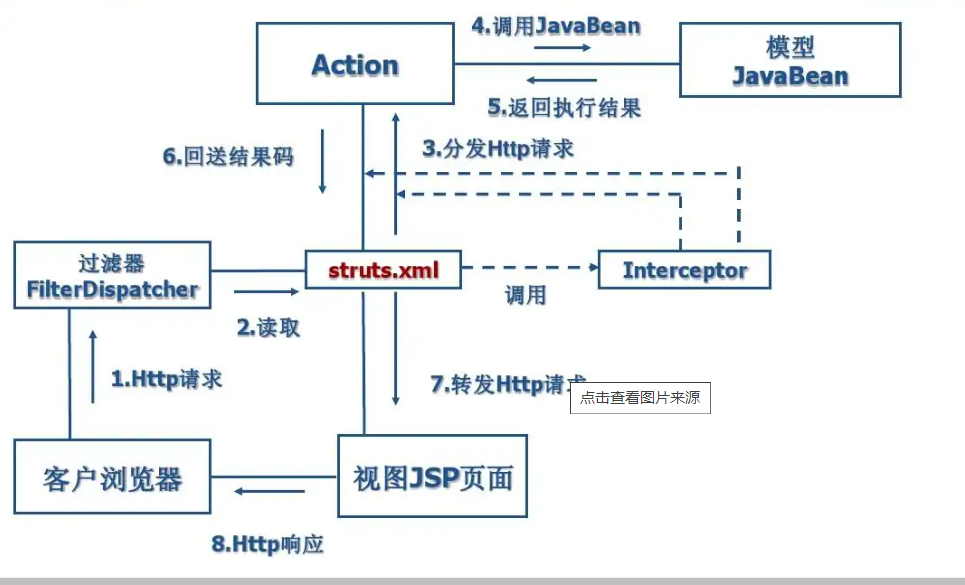
S2-001
Struts2 对 OGNL 表达式的解析使用了开源组件 opensymphony.xwork 2.0.3,所以实际上这是一个 xwork 组件的漏洞,影响了 Struts2。
参考链接:https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/WW/S2-001
该漏洞是因为Struts2的标签处理功能:altSyntax , 在该功能开启时 , 支持对标签中的Ognl表达式进行解析并执行。
而altSyntax在解析的时候 ,是依赖于开源组件xwork 。
漏洞gadget:
com.apache.struts2.views.jsp.ComponentTagSupport.doEndTag()org.apache.struts2.components.UIBean.end()org.apache.struts2.components.UIBean.evaluateParams()org.apache.struts2.components.Component.findValue()com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.TextParseUtil.translateVariables()com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.OgnlValueStack.findValue()com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.OgnlUtil.findValue()com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.Ognl.getValue()而在doEndTag之前 ,是doStartTag(),用于获取一些组件信息和属性赋值,总之是些初始化的工作。
搭建环境
编辑有漏洞的页面:
S2-001 demo web.xml配置如下:
struts2 org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher struts2 /* index.jsptest.OGNLTest.demo01Action
package test.OGNLTest;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;public class demo01Action extends ActionSupport { private String username = null; private String password = null; public demo01Action() { } public String getUsername() { return this.username; } public String getPassword() { return this.password; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public String execute() throws Exception { if (!this.username.isEmpty() && !this.password.isEmpty()) { return this.username.equalsIgnoreCase("admin") && this.password.equals("admin") ? "success" : "error"; } else { return "error"; } }}/resources/struts.xml配置如下:
<!----> <!-- --> /welcome.jsp /index.jsp welcome.jsp:
TEST hello , 因为在web.xml中配置了struts的filter , 在处理请求时 ,会进入org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher
OGNL的使用此处不再赘述。
漏洞利用POC:
%{@java.lang.System @getProperty("user.dir")}
漏洞触发关键点:
FilterDispatcher.doFilter()会调用Dispatcher.serviceAction() ,该方法是核心方法:
首先会调用createContextMap 来获取HttpServletRequest 和 HttpServletResponse 和 ServletContext , 并将其放入extraContext中。
Map extraContext = this.createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
try { UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey); String namespace = mapping.getNamespace(); String name = mapping.getName(); String method = mapping.getMethod(); Configuration config = this.configurationManager.getConfiguration(); ActionProxy proxy = ((ActionProxyFactory)config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class)).createActionProxy(namespace, name, extraContext, true, false); //此处创建Action代理类 proxy.setMethod(method); request.setAttribute("struts.valueStack", proxy.getInvocation().getStack()); //此处创建了DefaultActionInvocation 的实例 if (mapping.getResult() != null) { Result result = mapping.getResult(); result.execute(proxy.getInvocation()); } else { proxy.execute(); } if (stack != null) { request.setAttribute("struts.valueStack", stack); } }之后通过createActionProxy 来创建Action代理类 ,在这过程中也会创建 DefaultActionInvocation 的实例,并通过其 createContextMap() 方法创建一个 OgnlValueStack 实例,并将 extraContext 全部放入 OgnlValueStack 的 context 中。

之后 , 调用了proxy.execute() 来将DefalutActionInvocation.InvocationContext放入了ActionContext中 :
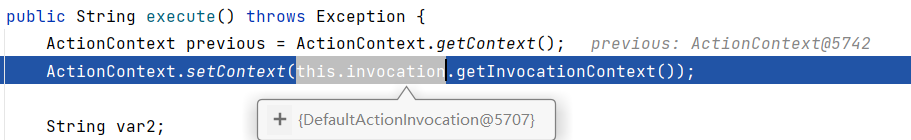
而在上述DefaultActionInvocation 初始化的时候 , 会调用DefaultActionInvocation .createAction(contextMap)

createAction又会调用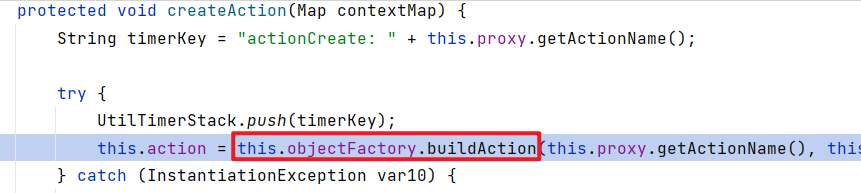
在ObjectFactory.buildAction中 , 调用了
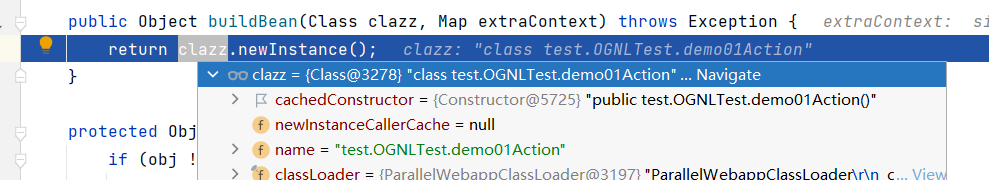
实例化了当前访问的类:demo01Action,并将其放入 OgnlValueStack 的 root 中。
在
this.dispatcher.serviceAction()方法的最后,执行创建的 ActionProxy 实例的execute()方法,调用创建的 DefaultActionInvocation 的invoke()方法,调用程序配置的各个 interceptors 的doIntercept()方法执行相关逻辑,其中的一个拦截器是 ParametersInterceptor,这个拦截器会在本次请求的上下文中取出访问参数,将参数键值对通过 OgnlValueStack 的 setValue 通过调用OgnlUtil.setValue()方法,最终调用OgnlRuntime.setMethodValue方法将参数通过 set 方法写入到 action 中,并存入 context 中。
此时 OgnlValueStack 实例中 root 中的 Action 对象的参数值已经被写入了。
在循环执行 interceptors 结束后,DefaultActionInvocation 的
invoke()方法执行了invokeActionOnly()方法,这个方法通过反射调用执行了 action 实现类里的 execute 方法,开始处理用户的逻辑信息。
用户逻辑走完后,会调用 DefaultActionInvocation 的
executeResult()方法,调用 Result 实现类里的execute()方法开始处理这次请求的结果。
如果返回结果是一个 jsp 文件,则会调用 JspServlet 来处理请求,然后交由 Struts 来处理解析相关的标签。
在进行标签解析的时候 ,有两个方法:ComponentTagSupport#doStartTag 和 ComponentTagSupport#doEndTag
doStartTag是一些初始化的方法
而doEndTag , 是标签解析结束后要做的事情
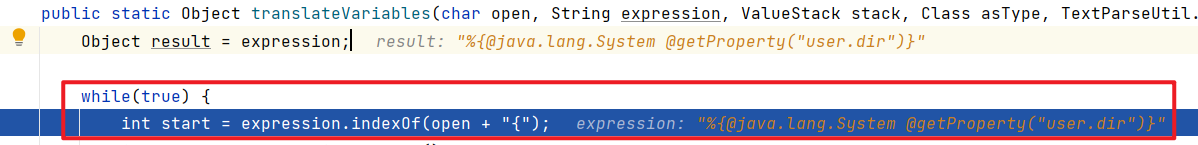
public int doEndTag() throws JspException { this.component.end(this.pageContext.getOut(), this.getBody()); this.component = null; return 6; }会调用 this.component.end()方法 , 最终触发点在TextParseUtil#translateVariables()方法 :
public static Object translateVariables(char open, String expression, ValueStack stack, Class asType, TextParseUtil.ParsedValueEvaluator evaluator) { Object result = expression; while(true) { int start = expression.indexOf(open + "{"); int length = expression.length(); int x = start + 2; int count = 1; while(start != -1 && x < length && count != 0) { char c = expression.charAt(x++); if (c == '{') { ++count; } else if (c == '}') { --count; } } int end = x - 1; if (start == -1 || end == -1 || count != 0) { return XWorkConverter.getInstance().convertValue(stack.getContext(), result, asType); } String var = expression.substring(start + 2, end); Object o = stack.findValue(var, asType); //关键点在这里 if (evaluator != null) { o = evaluator.evaluate(o); } String left = expression.substring(0, start); String right = expression.substring(end + 1); if (o != null) { if (TextUtils.stringSet(left)) { result = left + o; } else { result = o; } if (TextUtils.stringSet(right)) { result = result + right; } expression = left + o + right; } else { result = left + right; expression = left + right; } } }此处 , 使用了while(true) 来进行循环调用 ,先获取了标签的值 ,如username , 之后便使用stack.findValue(var, asType); 来查找username的值 (即为前端输入过来的值) , 之后便得到payload:%{@java.lang.System @getProperty("user.dir")} , 之后循环解析了标签中的变量名
之后即进入了

findValue中 ,最终会调用到OGNL.getValue() 来进行解析 , 从而触发漏洞
循环解析的过程 :
username –> %{username} –> %{@java.lang.System @getProperty(“user.dir”)} –> D:\Environment\apache-tomcat-9.0.52\bin
在第一次OGNL解析时 , 解析的是%{var} ,解析的实际上是标签中的变量名(根本原因:循环解析)