nginx配置文件rewrite和ifrewrite
语法:rewrite regex replacement flag;,如:
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 break;此处的$1用于引用(.*.jpg)匹配到的内容,又如:
rewrite ^/bbs/(.*)$ http://www.idfsoft.com/index.html redirect;如上例所示,replacement可以是某个路径,也可以是某个URL
常见的flag
| flag | 作用 |
|---|---|
| last | 基本上都用这个flag,表示当前的匹配结束,继续下一个匹配,最多匹配10个到20个 一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,就不再被后面其它的rewrite规则进行处理 而是由UserAgent重新对重写后的URL再一次发起请求,并从头开始执行类似的过程 |
| break | 中止Rewrite,不再继续匹配 一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,由UserAgent对新的URL重新发起请求, 且不再会被当前location内的任何rewrite规则所检查 |
| redirect | 以临时重定向的HTTP状态302返回新的URL |
| permanent | 以永久重定向的HTTP状态301返回新的URL |
rewrite模块的作用是用来执行URL重定向。这个机制有利于去掉恶意访问的url,也有利于搜索引擎优化(SEO)
nginx使用的语法源于Perl兼容正则表达式(PCRE)库,基本语法如下:
| 标识符 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| ^ | 必须以^后的实体开头 |
| $ | 必须以$前的实体结尾 |
| . | 匹配任意字符 |
| [] | 匹配指定字符集内的任意字符 |
| [^] | 匹配任何不包括在指定字符集内的任意字符串 |
| | | 匹配 | 之前或之后的实体 |
| () | 分组,组成一组用于匹配的实体,通常会有 | 来协助 |
//创建images目录,用于存放图片[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/[root@nginx html]# mkdir images//images中存放一张图片[root@nginx html]# ls images/1.jpg//修改配置文件添加location[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf/[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf location /images { root html; }[root@nginx conf]# systemctl restart nginx浏览器访问
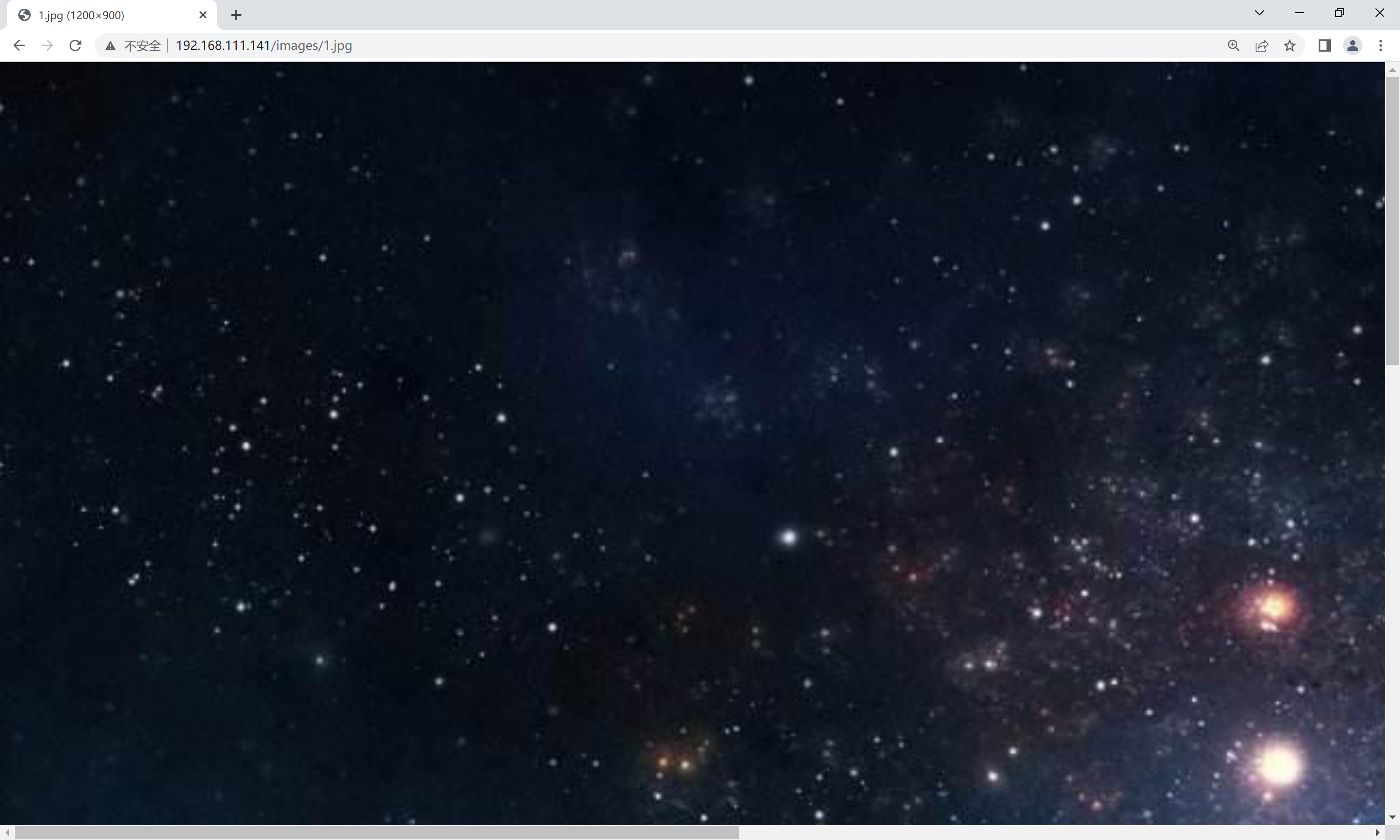
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html/[root@nginx html]# ls50x.html abc images index.html[root@nginx html]# mv images imgs//正常情况下当修改了目录名 就不能[root@nginx html]# ls50x.html abc imgs index.html[root@nginx conf]# pwd/usr/local/nginx/conf[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*)$ /imgs/$1 break;//所有以images开头访问的 用imgs响应 }[root@nginx conf]# systemctl restart nginx浏览器访问images/1.jpg
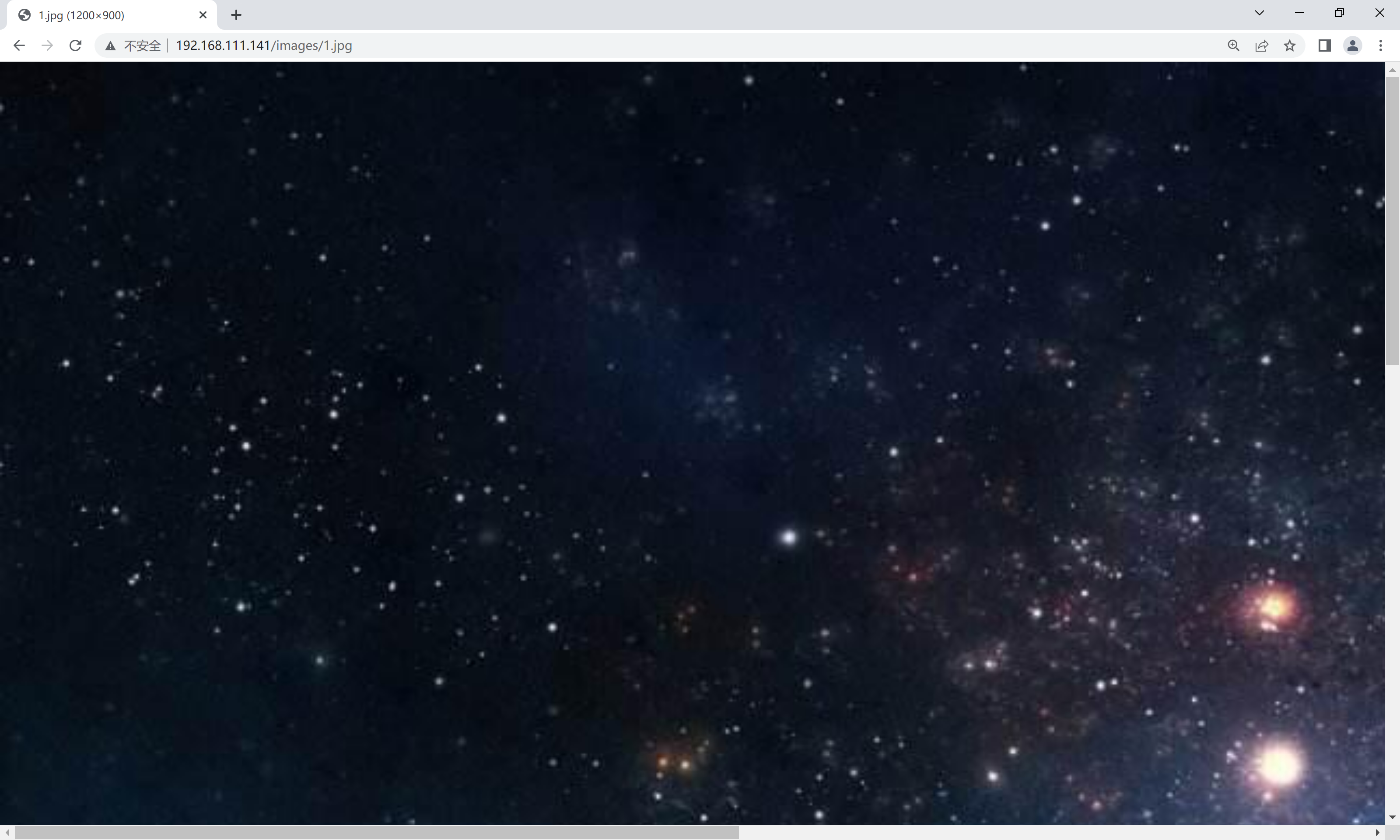
使用imgs/1.jpg也可以访问
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ https://t7.baidu.com/it/u=2511982910,2454873241&fm=193&f=GIF break;//将响应换为网页图片的地址 }[root@nginx conf]# systemctl restart nginx浏览器访问images/1.jpg 跳转到了网页图片
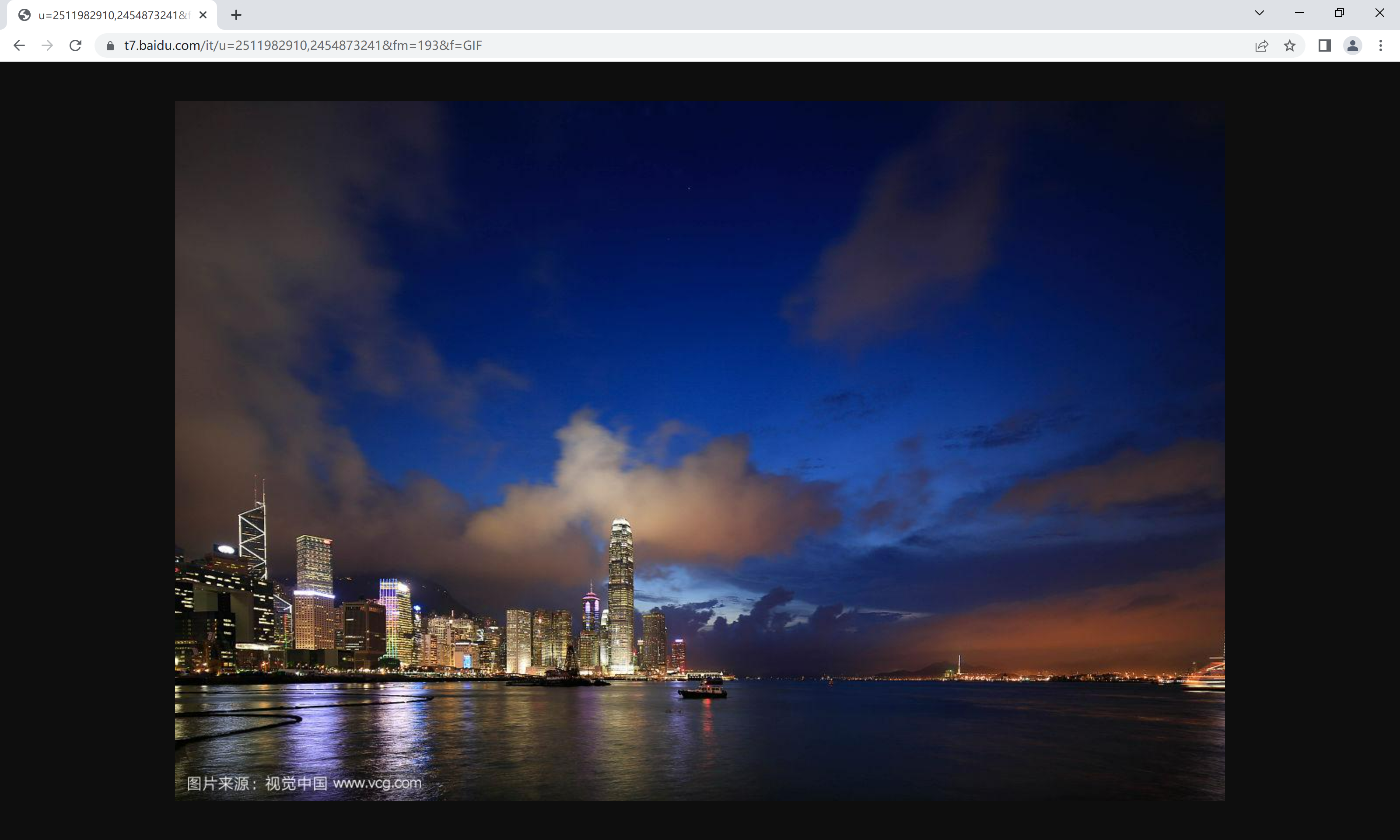
当前匹配结束 继续匹配下一个
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 last; } location /imgs { rewrite ^/imgs/(.*\.jpg)$ http://www.baidu.com break; }[root@nginx conf]# systemctl restart nginx访问images/1.jpg 进行下一个匹配 跳转到百度
redirect临时重定向
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 redirect; }[root@nginx conf]# systemctl restart nginx
permanent永久重定向
[root@nginx conf]# vim nginx.conf location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 permanent; } location /imgs { rewrite ^/imgs/(.*\.jpg)$ http://www.baidu.com break; } [root@nginx conf]# systemctl restart nginx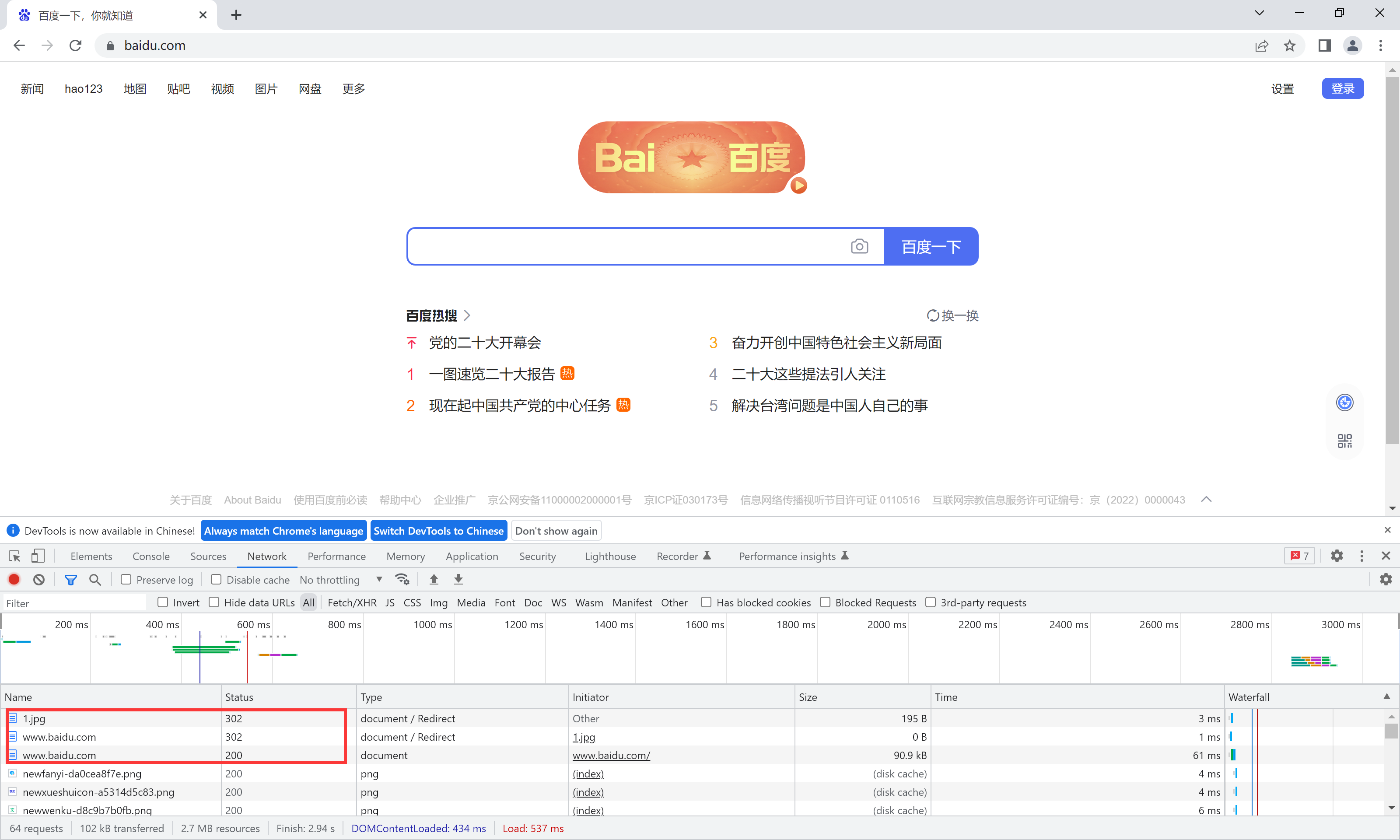
if
语法:if (condition) {…}
应用场景:
- server段
- location段
常见的condition
- 变量名(变量值为空串,或者以“0”开始,则为false,其它的均为true)
- 以变量为操作数构成的比较表达式(可使用=,!=类似的比较操作符进行测试)
- 正则表达式的模式匹配操作
- ~:区分大小写的模式匹配检查
- ~*:不区分大小写的模式匹配检查
- !和!*:对上面两种测试取反
- 测试指定路径为文件的可能性(-f,!-f)
- 测试指定路径为目录的可能性(-d,!-d)
- 测试文件的存在性(-e,!-e)
- 检查文件是否有执行权限(-x,!-x)
基于浏览器实现分离案例
if ($http_user_agent ~ Firefox) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /firefox/$1 break;} if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break;} if ($http_user_agent ~ Chrome) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /chrome/$1 break;}防盗链案例
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|jpeg|png)$ { valid_referers none blocked www.wxh.world; //只有从页面点击的图片是有效链接 if ($invalid_referer) { rewrite ^/ http://www.baidu.coml;//无效链接直接从写URL到百度 }}